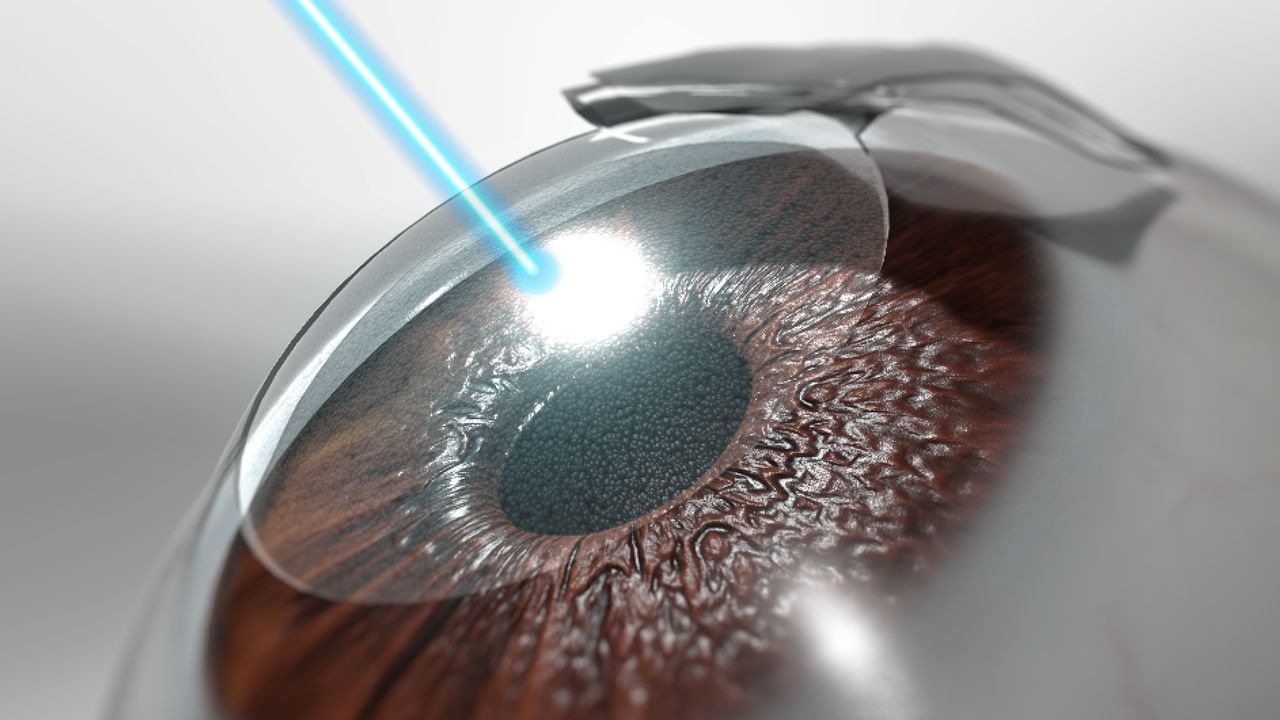
Introduction: Understanding Cataracts and the Need for Surgery
Cataracts are one of the most common causes of vision impairment, especially as we age. A cataract forms when the natural lens of the eye becomes cloudy, preventing light from passing through clearly. This results in blurry vision, glare, and difficulty seeing in low light conditions. For some, cataracts are a natural part of the aging process, but when they start affecting your ability to perform everyday tasks, cataract surgery may be necessary.
In this article, we will explore the signs that may indicate you need cataract surgery and guide you on when to take action. We’ll break down the process, from the symptoms you might experience to the recovery steps following the surgery. By the end, you’ll have a clearer understanding of what to expect and when to seek treatment.
What Is Cataract Surgery?
Cataract surgery is a procedure that removes the cloudy lens from the eye and replaces it with a clear artificial intraocular lens (IOL). This surgery restores vision and helps to improve the overall quality of life for individuals who have cataracts that interfere with daily activities. It is typically done on an outpatient basis, meaning you can go home the same day.
The procedure itself is quick, lasting about 15 to 30 minutes, and is generally very safe. The majority of patients experience improved vision shortly after the surgery, although full recovery may take several weeks.
Before Cataract Surgery
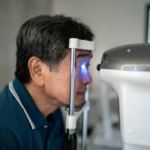
Pre-Surgery Eye Tests
Before cataract surgery, your eye doctor will conduct a series of tests to determine the severity of the cataract and assess the health of your eye. These tests are essential for planning the surgery and ensuring the best possible results.
- Vision Test: This helps determine how much your vision is affected by the cataract.
- Eye Measurements: Your doctor will measure the shape and size of your eye, which will help them choose the best intraocular lens (IOL) for your needs.
- Corneal and Retinal Health Check: These tests help ensure there are no other underlying conditions in the eye that could affect your recovery or post-surgery vision.
These tests usually take about an hour and are non-invasive, providing your surgeon with the information they need to proceed with the surgery.
Preparation Steps
In the days leading up to your surgery, there are a few things you need to do to prepare:
- Stop Certain Medications: You may need to stop taking medications like blood thinners a few days before surgery to reduce the risk of complications.
- Use Prescribed Eye Drops: You’ll likely be given eye drops to prevent infection and reduce inflammation before the surgery.
- Fasting: For certain types of anaesthesia, you may be asked not to eat or drink anything for several hours before the surgery.
Your surgeon will provide you with detailed instructions on how to prepare in the days before surgery, so it’s important to follow them closely.
What Patients Should and Shouldn’t Do
Here are some basic guidelines for what to do—and what to avoid—before cataract surgery:
- Do: Follow the doctor’s instructions regarding medications, eye drops, and fasting.
- Don’t: Wear makeup or eye makeup on the day of surgery, as this can increase the risk of infection.
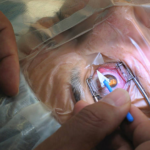
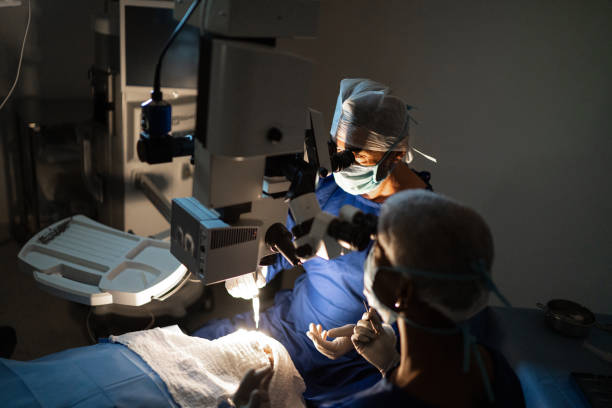
During Cataract Surgery
How the Procedure Is Performed
Cataract surgery is a straightforward procedure that usually takes between 15 and 30 minutes. Here’s what happens during the surgery:
- Anaesthesia: The eye is numbed with local anaesthesia. You’ll be awake during the procedure, but you won’t feel any pain. Sometimes, a mild sedative is given to help you relax.
- Incision: The surgeon makes a small incision in the cornea (the clear outer layer of the eye) to access the cloudy lens.
- Cataract Removal: The cloudy lens is broken up using ultrasound or a laser, a process known as phacoemulsification, and then the pieces are removed.
- Lens Insertion: An artificial intraocular lens (IOL) is inserted into the lens capsule, where the natural lens once was. The IOL helps focus light onto the retina to restore clear vision.
- Closing the Incision: The small incision usually doesn’t require stitches, as it heals on its own.
Pain Management and Duration

The procedure itself is usually painless due to local anaesthesia. Most patients feel mild pressure but no significant discomfort. The surgery typically lasts only 15 to 30 minutes, and you will be awake throughout.
What Patients Experience During Surgery
During cataract surgery, you may see light or shadows and feel pressure in the eye, but it’s common to feel relaxed and comfortable throughout the procedure. The sedative, if given, ensures you are calm and still, allowing the surgeon to work with precision.
After Cataract Surgery
Recovery Timeline
Cataract surgery recovery is relatively fast, with most patients noticing significant improvements in their vision within a few days. However, full recovery may take several weeks. Here’s what to expect:
- First 24-48 Hours: You may experience some discomfort or a gritty feeling in your eye. Your vision may be blurry at first, but it will improve gradually.
- Week 1: Your vision will likely improve significantly, although you may still experience some sensitivity to light and glare. It’s common to have fluctuating vision during the first week.
- Week 2-4: By this time, your eye will be healing, and your vision will stabilize. Most people can return to normal activities by the end of the first month, although heavy lifting and strenuous activities should be avoided.
- 6-8 Weeks: Full recovery typically occurs within 6 to 8 weeks. Some patients may still need glasses for close-up tasks, but most find they no longer need glasses for distance vision.
Vision Changes
Most people experience clear vision shortly after cataract surgery. You may notice immediate improvements in your ability to see in low-light conditions and reduced glare from headlights or streetlights. Some patients report seeing brighter colors as well.
While your vision will be significantly improved, some people may still need reading glasses for close-up work, depending on the type of intraocular lens (IOL) chosen.
Post-Operative Care and Restrictions
After cataract surgery, it’s important to follow the post-operative care instructions to ensure a smooth recovery:
- Use Eye Drops: Your doctor will prescribe eye drops to reduce inflammation and prevent infection. It’s important to follow the schedule precisely.
- Avoid Rubbing Your Eye: For the first few weeks, you should avoid rubbing or pressing on your eye to prevent irritation or complications.
- Wear Protective Shield: You may be asked to wear an eye shield at night to protect the eye while you sleep.
- Avoid Strenuous Activity: Refrain from heavy lifting or vigorous exercise for a few weeks to avoid straining your eyes.
Benefits and Success Rates
Cataract surgery is one of the most successful surgeries performed worldwide, with more than 95% of patients experiencing improved vision. The benefits include:
- Improved Vision: Most people notice significant improvements in vision, particularly in low-light conditions and for activities like driving and reading.
- Quick Recovery: The recovery process is relatively short, with many people resuming normal activities within a few weeks.
- Increased Quality of Life: Cataract surgery can help you regain the independence you may have lost due to poor vision, allowing you to enjoy activities and experiences you may have been avoiding.
Possible Risks and Side Effects
While cataract surgery is generally safe, there are a few potential risks and side effects:
- Infection: Although rare, infection can occur. It’s essential to follow your doctor’s instructions regarding post-surgery care to minimize the risk.
- Inflammation: Some inflammation or swelling in the eye is common, but it usually resolves with prescribed eye drops.
- Vision Changes: A small percentage of patients may experience glare, halos, or fluctuating vision after surgery, but these symptoms typically improve over time.
- Retinal Detachment: Though rare, retinal detachment can occur and may require immediate medical attention.
When to Contact Your Eye Doctor
You should contact your doctor if you experience any of the following:
- Severe Pain: If you experience significant pain that doesn’t improve with prescribed medication, contact your eye doctor.
- Sudden Vision Loss: Any sudden or severe loss of vision should be addressed immediately.
- Increased Redness or Swelling: If redness or swelling in the eye worsens after surgery, seek medical advice.
- Flashes of Light or Floaters: These could indicate a retinal issue, which requires prompt attention.
Conclusion: Reassurance and Action
Cataract surgery can be life-changing, offering restored vision and improved quality of life. Recognizing the signs that you may need cataract surgery and understanding the process will help you feel more comfortable about the procedure.
If you’re experiencing blurry vision, difficulty with night driving, or glare from lights, it may be time to discuss cataract surgery with your doctor. The surgery is safe, effective, and typically results in dramatic improvements in vision.
Don’t wait too long to take action. Early intervention can help you maintain your independence and improve your overall quality of life.
FAQs
1. How do I know when I need cataract surgery?
If cataracts are causing blurry vision, difficulty with night driving, or sensitivity to light that affects daily tasks, it may be time to consider surgery. Your eye doctor can help you assess the severity of your cataracts and determine if surgery is necessary.
2. Is cataract surgery painful?
Cataract surgery is typically painless because the eye is numbed with local anaesthesia. You may feel mild pressure during the procedure, but it should not be painful. Any discomfort after surgery is usually mild and temporary.
3. How soon after surgery will I notice improved vision?
Many patients experience improved vision within a few days after cataract surgery. While vision improves quickly, it may take several weeks for it to stabilize fully. You may still need glasses for reading or close-up tasks depending on the type of IOL used.
4. What are the risks of cataract surgery?
Although cataract surgery is generally safe, risks include infection, inflammation, glare or halos, and, in rare cases, retinal detachment. Following your doctor’s post-operative care instructions significantly reduces these risks.
5. Can I drive immediately after cataract surgery?
You should avoid driving on the day of surgery and for a few days afterward. Your vision may be blurry during the initial recovery phase. Most people are able to drive again after about a week, but always follow your doctor’s guidance based on your recovery.